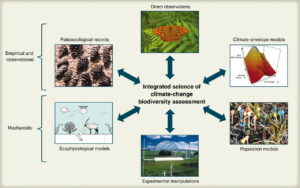
Forest biodiversity plays a pivotal role in maintaining ecological balance and supporting human livelihoods. This article delves into the significance of forest biodiversity in combating climate change and sustaining livelihoods, highlighting the need for conservation efforts and sustainable practices.
Understanding Forest Biodiversity
Forest biodiversity encompasses the variety of life forms within forest ecosystems, including plants, animals, fungi, and microorganisms. This diversity is essential for ecosystem health and resilience, providing numerous ecosystem services such as carbon sequestration, water purification, and soil fertility. Forests cover about 31% of the Earth’s land area, harboring 80% of terrestrial species and playing a critical role in maintaining global biodiversity.
The Role of Forest Biodiversity in Climate Change Mitigation
Carbon Sequestration
Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing and storing carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere. Trees and other vegetation capture CO2 through photosynthesis, converting it into biomass and releasing oxygen. This process helps mitigate climate change by reducing the concentration of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. Diverse forests with a variety of species and ages are more effective at sequestering carbon, as different species contribute to different stages of carbon storage.
Resilience to Climate Change
Biodiverse forests are more resilient to the impacts of climate change, such as extreme weather events, pests, and diseases. A diverse range of species enhances the stability and adaptability of forest ecosystems, allowing them to recover from disturbances more quickly. This resilience is crucial for maintaining the ecosystem services that forests provide, such as water regulation and soil protection, which are vital for human livelihoods.
Forest Biodiversity and Livelihoods
Supporting Local Communities
Forests are home to approximately 1.6 billion people, including indigenous communities who rely on forest resources for their livelihoods. These communities depend on forests for food, medicine, shelter, and income. Forest biodiversity ensures the availability of a wide range of resources, supporting diverse livelihoods and cultural practices. Sustainable management of forest resources is essential for the well-being of these communities and the preservation of their traditional knowledge.
Economic Value
Forests contribute significantly to the global economy, providing raw materials for industries such as timber, pharmaceuticals, and tourism. Biodiversity-rich forests offer a variety of non-timber forest products (NTFPs) such as fruits, nuts, resins, and medicinal plants, which generate income for local communities and contribute to food security. Ecotourism, based on the conservation of forest biodiversity, is an important source of revenue for many countries, promoting sustainable development and conservation efforts.
Threats to Forest Biodiversity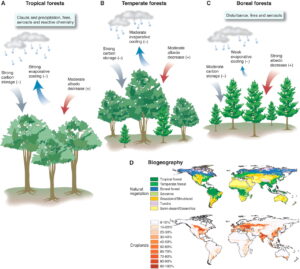
Deforestation and Land Use Change
Deforestation, driven by agricultural expansion, logging, and infrastructure development, is a major threat to forest biodiversity. The conversion of forests to agricultural land and urban areas leads to habitat loss, fragmentation, and degradation, reducing the capacity of forests to support diverse species and ecosystem services. Sustainable land-use practices and reforestation efforts are essential to counteract these impacts and restore forest biodiversity.
Climate Change
Climate change poses a significant threat to forest biodiversity, altering temperature and precipitation patterns, and increasing the frequency and intensity of extreme weather events. These changes can disrupt the distribution and behavior of species, leading to shifts in forest composition and structure. Conservation strategies must address the impacts of climate change on forest ecosystems, promoting adaptive management practices and the restoration of degraded areas.
Conservation and Sustainable Management
Protected Areas and Conservation Strategies
Establishing protected areas is a key strategy for conserving forest biodiversity. These areas safeguard critical habitats and provide refuges for threatened species. Conservation strategies should also focus on connecting fragmented forests through ecological corridors, enhancing the genetic diversity and resilience of forest ecosystems. Community-based conservation initiatives, involving local communities in the management and protection of forests, are essential for the success of conservation efforts.
Sustainable Forest Management
Sustainable forest management (SFM) practices aim to balance the ecological, social, and economic functions of forests. SFM includes practices such as selective logging, agroforestry, and the certification of forest products, which ensure the sustainable use of forest resources while maintaining biodiversity. Promoting the use of NTFPs and supporting sustainable livelihoods for forest-dependent communities are crucial components of SFM, contributing to both conservation and poverty alleviation.
Conclusion
Forest biodiversity is a cornerstone of global ecological health and human well-being. Its role in combating climate change and sustaining livelihoods underscores the need for urgent conservation and sustainable management efforts. By protecting and restoring forest biodiversity, we can enhance the resilience of forest ecosystems, support local communities, and contribute to a sustainable future for all.
Conserving forest biodiversity is not just an environmental imperative; it is a socio-economic necessity that requires global cooperation and commitment. Sustainable practices, informed policies, and community engagement are essential to safeguard the biodiversity of our forests and ensure the continued provision of their invaluable services.
“