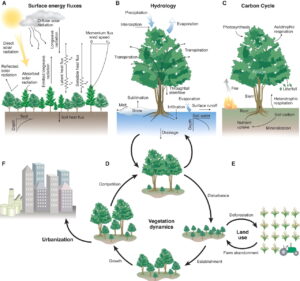
As the world grapples with the challenges of climate change and rapid urbanization, the concept of climate-smart forest economies is emerging as a pioneering force in sustainable urban development. By integrating sustainable forestry practices with urban planning, these economies offer a promising solution to mitigate environmental impact while fostering economic growth. This article delves into the role of climate-smart forest economies in driving sustainable urban development, exploring their benefits, key practices, and future potential.
Understanding Climate-Smart Forest Economies
Climate-smart forest economies are based on the principle of managing forests in a way that maximizes their carbon sequestration capabilities while providing economic and social benefits. These economies emphasize sustainable forest management, conservation, and restoration, ensuring that forests continue to function as vital carbon sinks. By doing so, they help combat climate change, support biodiversity, and sustain local communities.
Key Practices in Climate-Smart Forestry
- Sustainable Forest Management: This involves the careful planning and management of forest resources to meet current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet theirs. Techniques include selective logging, maintaining tree cover, and promoting the growth of native species.
- Forest Conservation and Restoration: Protecting existing forests and restoring degraded ones are critical components. Conservation efforts focus on preventing deforestation and degradation, while restoration projects aim to bring back forests to their natural state, enhancing biodiversity and carbon sequestration.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees into agricultural landscapes provides multiple benefits, such as improving soil health, enhancing water retention, and increasing crop yields. This practice also contributes to carbon sequestration and diversifies income sources for farmers.
- Community-Based Forest Management: Empowering local communities to manage forest resources ensures that the benefits of sustainable forestry practices are shared equitably. It also fosters a sense of ownership and responsibility towards forest conservation.
Benefits of Climate-Smart Forest Economies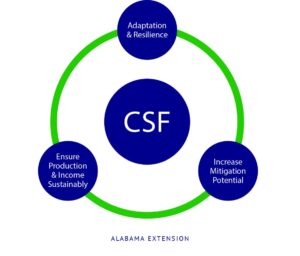
- Carbon Sequestration: Forests play a crucial role in absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. By maintaining and expanding forest cover, climate-smart forest economies help reduce greenhouse gas concentrations, mitigating climate change.
- Biodiversity Conservation: Forests are home to a significant portion of the world’s biodiversity. Sustainable forestry practices ensure the preservation of these ecosystems, supporting a wide range of plant and animal species.
- Economic Growth: Sustainable forest management creates jobs and stimulates economic activities in rural areas. It also provides raw materials for various industries, contributing to economic diversification.
- Urban Resilience: Integrating green spaces and urban forests into city planning enhances urban resilience. Trees in urban areas reduce the heat island effect, improve air quality, and provide recreational spaces for residents.
Case Studies: Leading Examples
- Costa Rica: Known for its progressive environmental policies, Costa Rica has implemented successful reforestation and conservation programs. The country has managed to increase its forest cover while promoting eco-tourism and sustainable agriculture.
- Finland: With its extensive forests, Finland has developed a robust bioeconomy. The country focuses on sustainable forest management, bioenergy, and the production of high-value forest products, contributing significantly to its GDP.
- Rwanda: Rwanda’s forest landscape restoration initiative aims to restore 2 million hectares of deforested and degraded land by 2030. This project not only enhances biodiversity but also supports the livelihoods of local communities.
The Future of Climate-Smart Forest Economies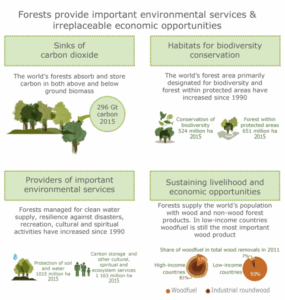
The integration of climate-smart forestry into urban development is a growing trend. As cities expand, incorporating forested areas and green infrastructure becomes increasingly important. Future advancements may include:
- Innovative Technologies: The use of remote sensing, drones, and satellite imagery for forest monitoring and management will enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of sustainable forestry practices.
- Policy Integration: Governments need to adopt policies that promote sustainable forestry and urban planning. Incentives for reforestation, conservation, and the use of sustainable building materials can drive the adoption of climate-smart practices.
- Public-Private Partnerships: Collaboration between governments, businesses, and non-governmental organizations can accelerate the development and implementation of climate-smart forest economies.
- Education and Awareness: Raising awareness about the benefits of sustainable forestry and the importance of green urban development is crucial. Educational programs and public campaigns can foster a culture of sustainability.
Conclusion
Climate-smart forest economies hold the key to pioneering sustainable urban development. By harmonizing the relationship between forests and cities, these economies offer a holistic approach to addressing climate change, conserving biodiversity, and promoting economic growth. As we move towards a more sustainable future, the principles and practices of climate-smart forestry will undoubtedly play a vital role in shaping resilient and thriving urban landscapes.