The Healthy Forests Initiative (HFI) is a pivotal program aimed at preserving and rejuvenating forests. With increasing concerns over climate change and sustainable energy, innovative strategies within the HFI are focusing on utilizing biomass for sustainable energy. This article delves into the various facets of this initiative, examining how biomass is being harnessed to promote environmental sustainability while generating energy.
Understanding Biomass and Its Potential
Biomass refers to organic materials derived from plants and animals, which can be used as a renewable energy source. Unlike fossil fuels, biomass can be replenished within a human lifetime, making it a sustainable option for energy production. Common biomass materials include wood, agricultural residues, and animal manure. When these materials are processed, they release energy that can be used for heating, electricity, and even fuel.
The Role of Biomass in the Healthy Forests Initiative
The HFI aims to reduce wildfire risks, promote forest health, and enhance biodiversity. Biomass plays a crucial role in this context by offering a sustainable method to manage forest residues. Dead trees, branches, and other forest debris, which are potential fire hazards, can be collected and converted into biomass energy. This not only reduces the risk of wildfires but also contributes to energy production.
Innovative Biomass Utilization Strategies
1. Forest Thinning and Biomass Harvesting
Forest thinning involves selectively removing trees to improve forest health and reduce competition among the remaining trees. This process generates a significant amount of biomass that can be harvested and utilized for energy. By integrating forest thinning with biomass energy production, the HFI ensures that forest management activities are both economically and environmentally sustainable.
2. Advanced Biomass Conversion Technologies
Modern technologies have revolutionized biomass conversion, making it more efficient and environmentally friendly. Pyrolysis, gasification, and anaerobic digestion are some advanced methods used to convert biomass into energy. These technologies not only maximize energy output but also minimize emissions, aligning with the goals of the HFI to promote clean energy.
3. Biomass Co-firing in Existing Power Plants
Another innovative strategy is co-firing biomass with coal in existing power plants. This approach leverages the existing infrastructure of coal plants while reducing greenhouse gas emissions. By gradually increasing the proportion of biomass in the fuel mix, the transition to renewable energy becomes more feasible and cost-effective.
Economic and Environmental Benefits
Utilizing biomass for energy within the HFI offers numerous economic and environmental benefits:
1. Job Creation and Economic Development
The biomass industry creates jobs in rural areas, particularly in forest management, biomass harvesting, and processing. This economic boost supports local communities and promotes sustainable development.
2. Reduction in Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Biomass energy is considered carbon-neutral because the carbon dioxide released during combustion is offset by the carbon dioxide absorbed by plants during their growth. This significantly reduces the carbon footprint compared to fossil fuels, contributing to climate change mitigation.
3. Enhanced Forest Health and Biodiversity
By removing excess forest debris, biomass harvesting helps maintain healthier forests. This reduces the risk of severe wildfires and promotes biodiversity by allowing native species to thrive.
Challenges and Solutions
Despite its potential, the use of biomass for energy faces several challenges. These include high initial costs, logistical issues related to biomass collection and transportation, and public perception. However, strategic planning and investment in research and development can address these challenges.
1. Investing in Infrastructure
Developing efficient supply chains and investing in biomass processing facilities are crucial for overcoming logistical challenges. Public-private partnerships can play a vital role in building the necessary infrastructure.
2. Raising Public Awareness
Educating the public about the benefits of biomass energy and its role in forest management can help gain public support. Outreach programs and community involvement are essential for the success of biomass initiatives.
3. Government Policies and Incentives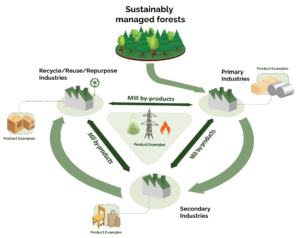
Supportive government policies and incentives can drive the growth of the biomass industry. Subsidies, tax credits, and grants for biomass projects encourage investment and innovation in this sector.
Conclusion
The Healthy Forests Initiative is pioneering innovative strategies to utilize biomass for sustainable energy. By integrating forest management with biomass energy production, the HFI promotes environmental sustainability, reduces wildfire risks, and supports rural economies. While challenges exist, strategic investments and public awareness can unlock the full potential of biomass, paving the way for a greener and more sustainable future.



