
Introduction
Forests are vital to the health of our planet, providing essential services such as carbon sequestration, biodiversity conservation, and climate regulation. However, as we move into 2024, the need to protect these vital ecosystems has become more pressing than ever. In this article, we will explore the latest trends and strategies for safeguarding forest ecosystems, highlighting innovative approaches and best practices for conservation.
Understanding the Importance of Forest Ecosystems
Before delving into protection strategies, it’s crucial to understand why forest ecosystems are so important:
- Carbon Sequestration: Forests play a key role in mitigating climate change by absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere.
- Biodiversity: Forests are home to more than 80% of the world’s terrestrial species, making them crucial for biodiversity conservation.
- Water Regulation: Forests help regulate the water cycle, prevent soil erosion, and maintain watershed health.
- Economic Value: Forests provide resources such as timber, food, and medicinal plants, supporting local economies.
Key Trends in Forest Ecosystem Protection for 2024
1. Leveraging Technology for Monitoring and Management
Advancements in technology are transforming how we monitor and manage forests. Key trends include:
- Satellite Monitoring: High-resolution satellites provide real-time data on deforestation, illegal logging, and forest health. Programs like NASA’s Landsat and the European Space Agency’s Copernicus are leading the way in satellite monitoring.
- Drones: Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are increasingly used for forest mapping, wildlife monitoring, and detecting illegal activities.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data to predict deforestation trends, assess forest health, and optimize conservation efforts.
2. Community Involvement and Indigenous Knowledge
Empowering local communities and incorporating indigenous knowledge are critical to effective forest conservation:
- Community-Based Conservation: Engaging local communities in forest management helps ensure that conservation strategies align with their needs and values. Initiatives such as community forest management (CFM) and collaborative conservation programs are gaining traction.
- Indigenous Rights: Recognizing and supporting indigenous land rights is essential. Indigenous communities often possess invaluable knowledge about forest ecosystems and sustainable practices. Legal recognition and support for their land management practices are crucial for conservation success.
3. Sustainable Forestry Practices
Promoting sustainable forestry practices is essential for maintaining forest health while meeting economic needs:
- Selective Logging: This method involves carefully selecting which trees to harvest, minimizing ecological impact and allowing forests to regenerate.
- Agroforestry: Integrating trees into agricultural systems can enhance biodiversity, improve soil health, and provide additional income for farmers.
- Certification Programs: Certifications like Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) ensure that forestry practices meet environmental and social standards.
4. Restoration and Reforestation Efforts
Restoring degraded forests and expanding forest cover are key strategies for ecosystem protection:
- Reforestation Projects: Initiatives aimed at planting trees in deforested areas help restore ecosystem functions and sequester carbon. Programs like the Bonn Challenge and the Great Green Wall are examples of large-scale reforestation efforts.
- Ecological Restoration: Beyond reforestation, ecological restoration involves rehabilitating degraded land to restore its natural functions and biodiversity.
5. Policy and Legislation
Effective policies and legislation are crucial for forest protection:
- Forest Protection Laws: Enforcing laws against illegal logging and land conversion is essential. Countries are increasingly strengthening their legal frameworks to protect forests.
- International Agreements: Global agreements such as the Paris Agreement and the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) play a role in setting targets and mobilizing resources for forest conservation.
6. Public Awareness and Education
Raising public awareness and educating people about forest conservation can drive collective action:
- Educational Campaigns: Initiatives to educate the public about the importance of forests and sustainable practices can increase support for conservation efforts.
- Citizen Science: Engaging the public in monitoring and reporting forest health through citizen science projects can enhance data collection and raise awareness.
Case Studies of Successful Forest Protection Strategies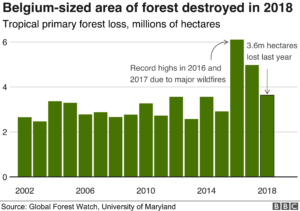
1. Amazon Fund (Brazil)
The Amazon Fund supports projects aimed at preventing deforestation and promoting sustainable land use in the Amazon rainforest. It has contributed to a significant reduction in deforestation rates in the region.
2. REDD+ Program
The Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD+) program provides financial incentives for developing countries to reduce emissions from deforestation and forest degradation. It has been successful in many countries, including Indonesia and Kenya.
3. Community Forest Management in Nepal
Nepal’s community forest management programs have empowered local communities to manage forest resources sustainably. This approach has led to improved forest health, increased biodiversity, and enhanced livelihoods.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite progress, several challenges remain:
- Climate Change: Rising temperatures and changing precipitation patterns pose threats to forest ecosystems.
- Illegal Activities: Illegal logging and land encroachment continue to undermine conservation efforts.
- Funding: Securing adequate funding for conservation projects remains a challenge.
Future directions include integrating climate adaptation strategies into forest management, enhancing international cooperation, and promoting innovative financing mechanisms.
Conclusion
Protecting forest ecosystems is a complex but essential task. By leveraging technology, involving communities, promoting sustainable practices, and enacting supportive policies, we can make significant strides in forest conservation. As we advance through 2024, continued innovation and collaboration will be key to ensuring the health and sustainability of our forests for generations to come.


