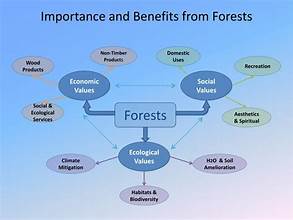
Forests, often regarded as the lungs of our planet, are not just vital for ecological balance but also serve as significant economic assets. As the world faces increasing environmental challenges and economic uncertainties, the role of sustainable forest management (SFM) in enhancing economic benefits has gained prominence. This article explores how sustainable forest management contributes to financial benefits and economic growth, providing insights into its value as a long-term investment.
Understanding Sustainable Forest Management (SFM)
Sustainable Forest Management (SFM) is a systematic approach aimed at managing forest resources in a way that meets current needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. SFM encompasses a range of practices, including selective logging, reforestation, and conservation efforts, all designed to maintain forest health, biodiversity, and productivity.
Key Principles of SFM
- Ecological Balance: Ensuring that forest management practices do not disrupt the ecological balance or lead to deforestation.
- Economic Viability: Managing forests in a way that supports local economies and generates revenue.
- Social Responsibility: Engaging with local communities and respecting their rights while managing forest resources.
- Long-Term Planning: Developing and implementing strategies that ensure forests’ health and productivity for future generations.
Financial Benefits of Sustainable Forest Management
1. Revenue Generation
SFM provides a steady stream of income through the sustainable harvesting of timber and non-timber products. Unlike conventional logging, which often leads to depletion, SFM practices ensure that forests remain productive over the long term. The revenue generated from sustainable timber harvesting can be substantial, providing funds for local governments and communities.
Case Study: Finland’s Forest Industry
Finland’s forest industry is a prime example of SFM’s economic benefits. The country’s approach to forest management has led to a thriving industry that contributes significantly to its GDP. Sustainable logging practices have allowed Finland to maintain a healthy forest ecosystem while generating substantial economic returns.
2. Job Creation
SFM creates jobs in various sectors, including forestry, conservation, and ecotourism. By investing in sustainable practices, forests can support employment opportunities that benefit local communities and contribute to economic stability. The creation of green jobs is an essential component of SFM, promoting both environmental sustainability and economic growth.
Case Study: The Amazon Rainforest
In the Amazon Rainforest, sustainable management practices have created jobs in eco-friendly industries such as sustainable agriculture and ecotourism. These jobs provide income for local communities while preserving the rainforest’s biodiversity.
3. Tourism Revenue
Forests are major attractions for ecotourism, which can be a significant source of revenue. Sustainable management practices enhance the beauty and accessibility of forested areas, attracting tourists who are willing to pay for guided tours, recreational activities, and nature experiences. The revenue from tourism can be reinvested into forest conservation and management efforts.
Case Study: Costa Rica’s Ecotourism
Costa Rica has leveraged its rich biodiversity and sustainable forest management practices to develop a robust ecotourism industry. The revenue generated from ecotourism has been used to fund conservation efforts and support local communities, demonstrating the economic potential of well-managed forests.
4. Carbon Sequestration
Forests play a crucial role in mitigating climate change by sequestering carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Sustainable forest management practices enhance this carbon storage capability, which can be monetized through carbon credit markets. By participating in carbon trading schemes, forest owners can generate additional income while contributing to global climate goals.
Case Study: REDD+ Program
The REDD+ (Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation) program provides financial incentives to countries that reduce emissions through sustainable forest management. By participating in REDD+, countries can earn carbon credits and receive funding for conservation initiatives, showcasing the financial benefits of carbon sequestration.
5. Enhanced Ecosystem Services
Forests provide a range of ecosystem services, including water purification, soil erosion control, and habitat provision for wildlife. Sustainable management practices ensure that these services are maintained, which can translate into financial benefits for industries and communities reliant on these ecosystem services. Investing in SFM helps preserve these valuable services, supporting long-term economic stability.
Case Study: The Watershed Protection in the United States
Forests in the United States play a vital role in watershed protection, providing clean water for millions of people. Sustainable forest management practices help maintain water quality and reduce the costs associated with water treatment and supply.
Challenges and Considerations
While the financial benefits of sustainable forest management are significant, there are challenges to consider:
- Initial Investment: Implementing SFM practices requires upfront investment in technology, training, and infrastructure.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to environmental regulations and certification standards can be complex and costly.
- Market Fluctuations: Revenue from forest products and ecosystem services can be affected by market fluctuations and economic conditions.
Overcoming Challenges
To overcome these challenges, stakeholders can collaborate to develop innovative solutions and strategies. For example, public-private partnerships can provide the necessary funding and expertise to implement SFM practices effectively. Additionally, governments can support SFM through incentives, subsidies, and policy frameworks that promote sustainable practices.
Conclusion
Forests represent a valuable economic asset that, when managed sustainably, can generate significant financial benefits. Sustainable Forest Management (SFM) enhances revenue through timber and non-timber products, creates jobs, boosts tourism, and contributes to carbon sequestration. By investing in SFM, societies can achieve economic growth while preserving the environmental and ecological value of forests.


