
In 2024, effective forest management has never been more crucial. The increasing pressures of climate change, biodiversity loss, and sustainable resource use are driving the need for innovative strategies to enhance forest ecosystems. This article explores contemporary forest management techniques that not only promote sustainability but also bolster biodiversity. By integrating these practices, we can ensure the health of our forests for future generations.
The Importance of Forest Management
Forests play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance. They act as carbon sinks, regulate the climate, support diverse wildlife, and provide resources for human communities. However, unsustainable logging, land conversion, and climate change are threatening these ecosystems. Effective forest management is essential to mitigate these threats and ensure that forests continue to provide their invaluable services.
Key Forest Management Strategies for 2024
1. Adaptive Management
Adaptive management is a systematic approach that uses monitoring and feedback to adjust practices based on the outcomes. This strategy involves:
- Continuous Monitoring: Collecting data on forest conditions, wildlife populations, and climate impacts.
- Flexible Practices: Adjusting management practices based on the latest data and changing conditions.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involving local communities, scientists, and policymakers in decision-making processes.
By adapting management practices in response to new information, forests can better withstand and recover from disturbances.
2. Ecological Restoration
Ecological restoration aims to return degraded forests to a more natural state. Techniques include:
- Reforestation: Planting native trees in deforested areas to restore forest cover.
- Habitat Restoration: Rebuilding critical habitats for endangered species.
- Soil and Water Conservation: Implementing practices to improve soil health and water quality.
Restoration efforts not only enhance biodiversity but also improve ecosystem services, such as water filtration and soil stabilization.
3. Sustainable Harvesting Practices
Sustainable harvesting ensures that forest resources are used in a way that does not deplete them or harm the ecosystem. Key practices include:
- Selective Logging: Removing only certain trees to maintain forest structure and promote regeneration.
- Reduced Impact Logging (RIL): Using techniques that minimize damage to the surrounding environment.
- Certification Schemes: Adopting standards like those from the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) to ensure responsible management.
These practices help maintain the ecological balance and ensure that forests remain productive and healthy.
4. Integrated Pest Management (IPM)
IPM involves using a combination of methods to control pests in an environmentally friendly way. Strategies include:
- Biological Control: Using natural predators to manage pest populations.
- Cultural Control: Altering forest management practices to reduce pest habitat.
- Mechanical Control: Employing physical methods, such as traps, to control pests.
By minimizing the reliance on chemical pesticides, IPM helps preserve the health of forest ecosystems and protect biodiversity.
5. Climate-Smart Forestry
Climate-smart forestry incorporates strategies to adapt to and mitigate the effects of climate change. This approach includes:
- Diverse Planting: Planting a variety of tree species to increase resilience to climate-related stresses.
- Carbon Sequestration: Enhancing forest capacity to capture and store carbon dioxide.
- Climate Monitoring: Tracking climate variables and their impacts on forest health.
By integrating these practices, forests can better adapt to changing climate conditions while contributing to global climate change mitigation efforts.
The Role of Technology in Modern Forest Management
Advancements in technology are revolutionizing forest management. Some key innovations include:
- Remote Sensing: Using satellites and drones to monitor forest health, track deforestation, and map habitats.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Analyzing spatial data to plan and manage forest resources effectively.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Predicting forest trends and optimizing management strategies through data analysis.
These technologies enhance our ability to manage forests more effectively and respond to emerging challenges.
Challenges and Future Directions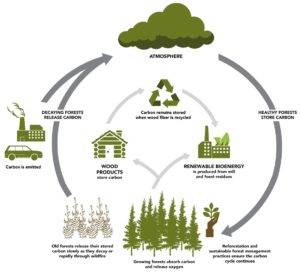
Despite the advances in forest management, several challenges remain:
- Funding and Resources: Adequate funding is needed to implement and sustain management practices.
- Policy and Regulation: Effective policies and regulations are essential for enforcing sustainable practices.
- Climate Change: Ongoing climate changes pose risks to forest health and require continuous adaptation.
Future forest management strategies must address these challenges by promoting collaboration among stakeholders, investing in research and technology, and adapting to evolving environmental conditions.
Conclusion
Effective forest management strategies are critical for enhancing biodiversity and sustainability in 2024. By adopting adaptive management, ecological restoration, sustainable harvesting practices, integrated pest management, and climate-smart forestry, we can ensure the health and resilience of our forests. Leveraging technology and addressing challenges through collaborative efforts will further support these goals. As we move forward, it is imperative to continue innovating and adapting our forest management practices to safeguard these vital ecosystems for future generations.


