Introduction
Biodiversity hotspots are regions with exceptionally high levels of endemic species that are also experiencing significant habitat loss. Recognized by conservationists and environmentalists, these areas are crucial for maintaining global health and climate resilience. This article delves into how these hotspots contribute to our planet’s health and stability, exploring their roles in ecological balance, human well-being, and climate adaptation.
Understanding Biodiversity Hotspots
Biodiversity hotspots are areas that harbor a rich variety of species, many of which are found nowhere else on Earth. To qualify as a hotspot, a region must have at least 1,500 species of vascular plants as endemics and it must have lost at least 70% of its original habitat. Examples include the Amazon Rainforest, the Coral Triangle, and the Madagascar and the Indian Ocean Islands.
Contributions to Global Health
- Medicinal Resources
Biodiversity hotspots are treasure troves of medicinal plants. Many modern pharmaceuticals are derived from compounds found in these regions. For example, the Amazon Rainforest has provided treatments for diseases like cancer, malaria, and high blood pressure. Preserving these hotspots ensures that we continue to have access to potential new medicines and treatments.
- Nutritional Benefits
The variety of plants and animals in biodiversity hotspots contributes to global food security. Many of the world’s staple crops, including fruits, vegetables, and nuts, originate from these regions. For instance, the Andes region in South America is the source of quinoa, a highly nutritious grain that has gained global popularity.
- Disease Regulation
Healthy ecosystems can act as buffers against disease. Biodiversity hotspots, through their diverse species, help regulate and control the spread of infectious diseases. For example, wetlands in these regions can reduce the prevalence of vector-borne diseases like malaria by supporting a range of species that keep mosquito populations in check.
Enhancing Climate Resilience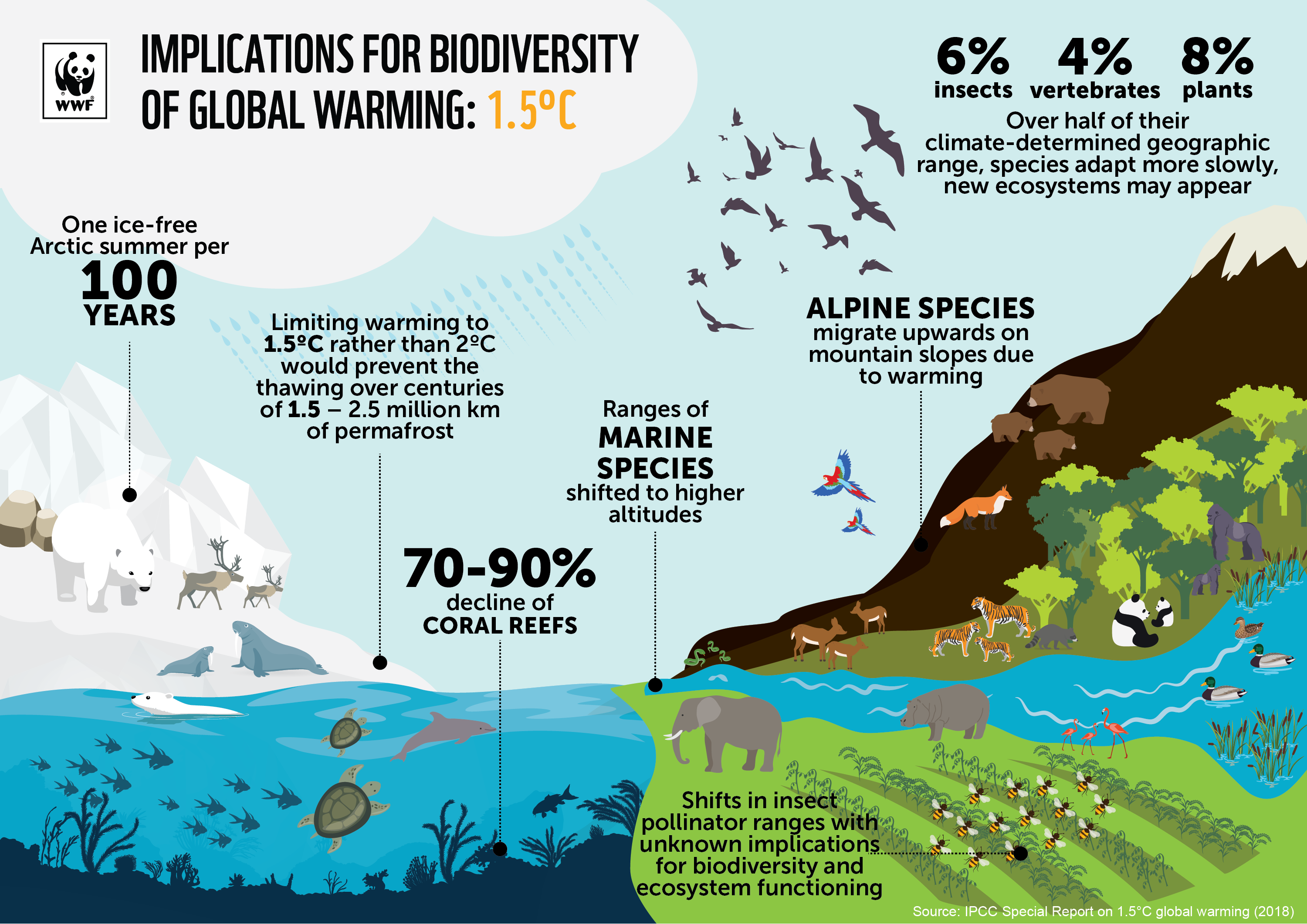
- Carbon Sequestration
Forests and other vegetation in biodiversity hotspots play a significant role in absorbing and storing carbon dioxide. The Amazon Rainforest alone stores a substantial portion of the world’s carbon. By maintaining these ecosystems, we can mitigate climate change and reduce the impact of greenhouse gases on global temperatures.
- Climate Regulation
Biodiversity hotspots contribute to climate regulation through their influence on local and global weather patterns. Forests, for example, affect rainfall patterns and temperature regulation. The Congo Basin, one of the largest tropical rainforests, helps stabilize regional climates by influencing weather patterns across Africa.
- Ecosystem Services
Ecosystems in biodiversity hotspots provide essential services such as water purification, soil fertility, and pollination. These services are vital for agriculture and human livelihoods. For instance, the coral reefs in the Coral Triangle provide critical habitat for marine species and protect coastlines from erosion, while also supporting fisheries that are crucial for food security in the region.
Challenges and Conservation Efforts
Despite their importance, biodiversity hotspots face numerous threats, including deforestation, climate change, and pollution. Conservation efforts are essential to protect these regions. Initiatives such as creating protected areas, enforcing anti-poaching laws, and promoting sustainable land use are crucial for maintaining the health and resilience of biodiversity hotspots.
- Protected Areas
Establishing protected areas helps safeguard critical habitats from destruction and exploitation. These areas can provide safe havens for endangered species and preserve essential ecological functions. For example, the establishment of national parks and reserves in biodiversity hotspots helps mitigate habitat loss and promotes species recovery.
- Sustainable Practices
Promoting sustainable agricultural and forestry practices helps reduce the impact of human activities on these ecosystems. Agroforestry, sustainable logging, and responsible tourism are strategies that can support conservation goals while providing economic benefits to local communities.
- Climate Action
Addressing climate change is crucial for protecting biodiversity hotspots. Reducing greenhouse gas emissions, transitioning to renewable energy sources, and supporting climate adaptation initiatives can help mitigate the effects of climate change on these sensitive areas.
Conclusion
Biodiversity hotspots are more than just areas of high species diversity; they are critical to global health and climate resilience. By providing medicinal resources, enhancing food security, and regulating climate, these regions play a vital role in maintaining the planet’s balance. Protecting and conserving these hotspots is essential for ensuring a healthy and resilient future for both people and the environment. Through concerted conservation efforts and sustainable practices, we can safeguard these invaluable regions and their contributions to global well-being.



