Introduction
Forestry agreements at the international level play a pivotal role in shaping global sustainable development. These agreements are designed to address deforestation, promote sustainable forest management, and combat climate change. By aligning with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), these agreements contribute to a healthier planet and a more equitable world. This article explores the influence of international forestry agreements on SDGs and how they drive global sustainability efforts.
Understanding International Forestry Agreements
International forestry agreements are treaties or frameworks developed through cooperation among countries to address forest-related issues. They aim to promote sustainable forest management, conserve biodiversity, and mitigate the effects of climate change. Key agreements include the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC), the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD), and the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) certification.
- UNFCCC and Forestry
The UNFCCC is a cornerstone in the global effort to combat climate change. Through its various protocols and mechanisms, such as the Kyoto Protocol and the Paris Agreement, it addresses forest conservation and afforestation. The Paris Agreement emphasizes the need for countries to implement strategies to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, which includes protecting and restoring forests. By aligning with the UNFCCC, countries commit to integrating forestry into their climate action plans, thereby contributing to SDG 13 (Climate Action).
- CBD and Biodiversity Conservation
The CBD focuses on the conservation of biological diversity, including forests. It aims to ensure the sustainable use of ecosystems and the fair and equitable sharing of benefits from genetic resources. Forests, as rich repositories of biodiversity, are critical to achieving SDG 15 (Life on Land). The CBD encourages member countries to develop national strategies for forest conservation and management, promoting practices that enhance biodiversity and ecosystem services.
- FSC Certification
The FSC provides a global certification system for responsible forest management. It sets standards for sustainable forestry practices and ensures that forest products are sourced from well-managed forests. FSC certification supports SDG 12 (Responsible Consumption and Production) by promoting sustainable supply chains and reducing the environmental impact of forest exploitation.
Impact on Sustainable Development Goals
International forestry agreements significantly contribute to several SDGs by addressing key areas of sustainability:
- Combating Climate Change (SDG 13)
Forests act as carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere and mitigating climate change. International agreements like the UNFCCC encourage countries to incorporate forestry into their climate strategies. By implementing reforestation and afforestation projects, countries can enhance their climate resilience and contribute to global emission reduction targets.
- Protecting Ecosystems and Biodiversity (SDG 15)
Forests are vital for maintaining biodiversity and supporting ecosystems. Agreements such as the CBD promote the protection of forest habitats and the sustainable use of forest resources. By safeguarding forests, these agreements help preserve diverse plant and animal species, maintain ecosystem services, and support local communities.
- Promoting Sustainable Consumption (SDG 12)
The FSC certification system plays a crucial role in promoting sustainable consumption patterns. By ensuring that forest products are sourced from responsibly managed forests, FSC certification helps reduce the ecological footprint of the forestry sector. This contributes to more sustainable production and consumption practices globally.
- Supporting Sustainable Economic Growth (SDG 8)
Sustainable forest management contributes to economic development by providing livelihoods and resources for communities. International agreements encourage practices that balance economic growth with environmental protection, ensuring that forest resources are used sustainably and equitably.
Challenges and Opportunities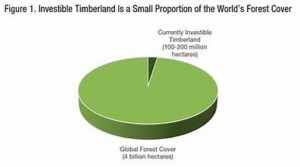
While international forestry agreements offer significant benefits, they also face challenges:
- Implementation and Compliance
Ensuring that countries adhere to forestry agreements can be challenging. Variability in national capacities and interests can affect the implementation of sustainable practices. Effective monitoring and enforcement mechanisms are essential to overcome these challenges.
- Balancing Development and Conservation
Striking a balance between economic development and forest conservation is often difficult. Countries may face pressure to exploit forest resources for short-term economic gains. International agreements must support policies that reconcile development needs with environmental protection.
- Funding and Resources
Adequate funding is crucial for implementing forestry agreements and achieving SDGs. Financial resources are needed for reforestation projects, conservation efforts, and capacity building. International cooperation and investment are necessary to address funding gaps.
Conclusion
International forestry agreements play a vital role in advancing sustainable development by addressing climate change, biodiversity loss, and sustainable resource management. By aligning with SDGs, these agreements foster global cooperation and drive progress toward a more sustainable and equitable world. As countries continue to face environmental and developmental challenges, the implementation and strengthening of these agreements will be crucial for achieving long-term sustainability goals.