
In recent years, national forest policies have become a cornerstone in the global effort to conserve biodiversity. These policies, which vary from country to country, aim to protect forest ecosystems, preserve wildlife habitats, and promote sustainable land use. Understanding their impact on biodiversity conservation is crucial for policymakers, environmentalists, and the general public. This article explores the key aspects of national forest policies and their implications for biodiversity conservation.
1. Understanding National Forest Policies
National forest policies are a set of regulations and guidelines developed by governments to manage and protect forest resources. These policies typically address various aspects, including forest management, land use, conservation strategies, and community involvement. The primary goals are to ensure sustainable forest management, mitigate deforestation, and enhance ecosystem resilience.
2. The Role of Forest Policies in Biodiversity Conservation
a. Habitat Protection
One of the most significant impacts of national forest policies is the protection of natural habitats. Forests serve as vital ecosystems for countless species of flora and fauna. By establishing protected areas and regulating land use, these policies help safeguard critical habitats from destruction and fragmentation. This protection is essential for maintaining biodiversity and supporting healthy populations of wildlife.
b. Sustainable Forest Management
Sustainable forest management is a key component of many national forest policies. This approach aims to balance the ecological, economic, and social functions of forests. By promoting practices such as selective logging, reforestation, and agroforestry, these policies help prevent overexploitation and ensure that forest resources are used in a way that supports long-term biodiversity conservation.
c. Restoration of Degraded Lands
Forest policies often include provisions for the restoration of degraded lands. Deforestation, pollution, and other human activities can lead to the loss of biodiversity and ecosystem services. National forest policies that focus on restoring degraded lands contribute to the recovery of ecosystems, which in turn benefits various species and enhances overall biodiversity.
d. Community Involvement and Indigenous Rights
Many national forest policies recognize the importance of involving local communities and indigenous peoples in forest management. These groups often have traditional knowledge and practices that contribute to effective conservation. By incorporating their input and respecting their rights, policies can enhance biodiversity conservation efforts and promote more equitable and sustainable land use.
3. Challenges and Limitations
Despite their benefits, national forest policies face several challenges and limitations:
a. Enforcement Issues
Effective enforcement of forest policies can be challenging due to limited resources, corruption, and lack of political will. Without proper enforcement, illegal logging, land encroachment, and other activities can undermine conservation efforts and lead to biodiversity loss.
b. Conflicting Interests
Forest policies often have to balance competing interests, such as economic development and conservation. In some cases, policies may prioritize economic gains over environmental protection, leading to conflicts that can negatively impact biodiversity.
c. Climate Change
Climate change poses a significant threat to forests and biodiversity. Changes in temperature, precipitation patterns, and the frequency of extreme weather events can affect forest ecosystems and the species that depend on them. National forest policies need to address climate change impacts to ensure effective biodiversity conservation.
4. Successful Examples of National Forest Policies
Several countries have implemented successful national forest policies that have positively impacted biodiversity conservation:
a. Costa Rica
Costa Rica is known for its progressive forest policies that emphasize conservation and sustainable management. The country has established a network of protected areas and has implemented payment for ecosystem services (PES) programs. These efforts have contributed to the recovery of forest cover and the protection of diverse ecosystems.
b. Sweden
Sweden’s forest policy focuses on sustainable forest management and biodiversity conservation. The country has a long history of integrating environmental considerations into forestry practices. Sweden’s approach includes maintaining a high percentage of forested land and implementing strict regulations to protect biodiversity.
c. New Zealand
New Zealand has developed national forest policies that prioritize both conservation and indigenous rights. The country has established several conservation areas and has recognized the role of Māori communities in forest management. This inclusive approach has led to successful biodiversity conservation outcomes.
5. Future Directions for National Forest Policies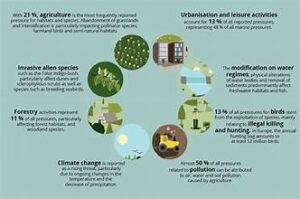
To enhance the effectiveness of national forest policies in biodiversity conservation, several future directions can be considered:
a. Integrating Ecosystem Services
National forest policies should increasingly incorporate ecosystem services into their frameworks. Recognizing the value of services such as carbon sequestration, water purification, and soil erosion control can help align conservation efforts with broader environmental and societal goals.
b. Enhancing Collaboration
Collaboration between governments, NGOs, local communities, and the private sector is essential for effective forest management. Strengthening partnerships and fostering multi-stakeholder engagement can improve policy implementation and outcomes.
c. Adapting to Climate Change
National forest policies need to address the impacts of climate change on forest ecosystems. This includes incorporating adaptive management strategies, promoting climate-resilient practices, and monitoring changes in forest conditions to inform policy adjustments.
6. Conclusion
National forest policies play a crucial role in biodiversity conservation by protecting habitats, promoting sustainable management, and involving communities. While challenges remain, successful examples from around the world demonstrate the potential for these policies to contribute significantly to preserving biodiversity. As we move forward, continued efforts to refine and strengthen forest policies will be essential for safeguarding our planet’s rich and diverse ecosystems.


